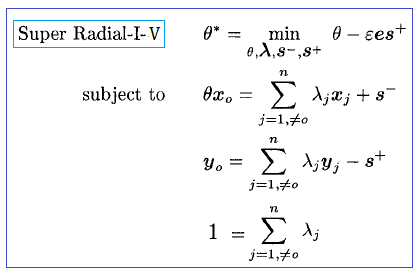
An important problem in the DEA literature is that of ranking those DMUs deemed efficient by the DEA model, all of which have a score of unity. One approach to the ranking problem is that provided by the super efficiency model of Andersen and Petersen (1993). The super-efficiency model involves executing the standard DEA models (CRS or VRS), but under the assumption that the DMU being evaluated is excluded from the reference set. In the input-oriented case, the model provides a measure of the proportional increase in the inputs for a DMU that could take place without destroying the ‘‘efficient” status of that DMU relative to the frontier created by the remaining DMUs. The super-efficiency score can also be thought of as a measure of stability. That is, if input data for instance, is subject to error or change over time, the super-efficiency score provides a means of evaluating the extent to which such changes could occur without violating that DMU’s status as an efficient unit. Hence, the score yields a measure of stability. It is well known that under certain conditions, the super efficiency DEA model may not have feasible solutions for efficient DMUs. As shown in Seiford and Zhu (1999a), infeasibility must occur in the case of the variable returns to scale (VRS) super-efficiency model. The input-oriented super efficiency model under constant returns to scale is expressed as:

The input-oriented super efficiency model under variable returns to scale is expressed as: